Investing in the North African Market in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Potential
Estimated reading time: 24 minutes
Key Points
- North Africa emerges as an attractive investment destination in 2025 with its economic dynamism, strategic location, and untapped potential.
- Key countries such as Egypt, Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia offer diverse opportunities in fintech, renewable energy, manufacturing, and resources.
- Investing in North Africa promises high returns, access to large markets, and an improving investment environment, but requires thorough research and appropriate strategies.
- Potential sectors include energy, manufacturing, agriculture, tourism, and technology, with emerging opportunities in agri-tech and climate-tech.
- Investors need to carefully navigate regulations, political-economic risks, and prioritize sustainability and innovation for long-term success.
Table of Contents
- Investing in the North African Market in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Potential
- Understanding the North African Investment Landscape and Investment Opportunities in Egypt
- Why Invest in North Africa? Growth Drivers and Competitive Advantages
- Key Sectors for Investment in North Africa: Harnessing Diverse Potential
- Navigating the Investment Process: Key Steps and Considerations
- Case Studies: Successful Investments in North Africa and Investment Opportunities in Egypt
- Risks and Challenges: Navigating a Complex Terrain
- Future Outlook for North African Investment and the Developing Industry in Algeria
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
The North African market is emerging as an increasingly attractive destination for international investors, especially as 2025 approaches. This appeal is not coincidental; it stems from the region’s growing economic vibrancy, strategic geographical position, and significant untapped potential across several key sectors. As global investors seek portfolio diversification and higher returns, Investing in the North African Market stands out as a promising option. The region offers unique opportunities but also comes with specific challenges that require careful consideration. This article will provide a comprehensive overview, guiding you through the advantages, top investment sectors, market entry steps, notable success stories, potential risks, and the future outlook for investing in North Africa. We will delve deeper into investment opportunities in Egypt, analyze Morocco’s real estate potential, and assess the developing industry in Algeria. With thorough preparation, as iHub Kenya highlighted in its 2025 investment review and outlook, investors can position themselves for success in one of the world’s most dynamic emerging markets.
Understanding the North African Investment Landscape and Investment Opportunities in Egypt
To make informed investment decisions, it is essential to grasp the overall economic and political landscape of the North African region. The region is not homogeneous but comprises multiple countries with distinct characteristics, creating a diverse and rich investment picture.

Overview of Key Countries for Investment
North Africa includes several prominent markets, each offering unique advantages and opportunities. Among them, Egypt, Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia are often the top destinations for international investors.
- Egypt: With a large population exceeding 100 million, Egypt not only provides a huge consumer market but also boasts a strong and rapidly developing financial technology (fintech) ecosystem. The Egyptian government has been implementing numerous economic reforms to attract foreign investment, focusing on large infrastructure projects like the Suez Canal Economic Zone. Investment opportunities in Egypt are particularly evident in the technology, manufacturing, and tourism sectors.
- Morocco: This country is recognized for its strategic location, serving as a bridge between Europe and sub-Saharan Africa. Morocco has invested heavily in infrastructure, including the Tanger Med port – one of the largest in the Mediterranean. The country is also increasingly focusing on developing renewable energy, especially solar energy, and building a competitive manufacturing industry, particularly in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
- Tunisia: Similar to Morocco, Tunisia also benefits from its favorable geographical location near Europe. The country has a skilled workforce and competitive labor costs, attracting investment in manufacturing, textiles, and information technology services. Tunisia is also working to develop its renewable energy sector and sustainable tourism.
- Algeria: Possessing abundant natural resources, especially oil and natural gas, Algeria is a magnet for large investments in the energy sector. The government is seeking to diversify the economy, opening up opportunities in other sectors such as agriculture, mining, and the pharmaceutical industry.
Regional Economic Indicators and Trends
According to forecasts, the North African region is expected to experience moderate but accelerating economic growth. A World Bank report indicates that the entire Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region is projected to grow by 2.6% in 2025 despite global uncertainties. The recovery in oil production and the easing of regional conflicts are expected to further boost North Africa’s GDP growth. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is even more optimistic, predicting that the region’s GDP growth could reach 3.6% in 2025, particularly if structural reforms continue to be implemented.
In addition, a notable trend is the strong push for digital technology adoption, sustainable development, and innovation across the region. Governments are recognizing the importance of digital transformation to enhance competitiveness and create new business models. This, coupled with a growing commitment to sustainability goals, is positioning the region for long-term development and opening up new investment avenues, as highlighted by iHub Kenya in its analysis of investment trends. This shift is not only creating opportunities in the technology and green energy sectors but also positively impacting traditional industries, forcing them to innovate to survive and thrive.

Why Invest in North Africa? Growth Drivers and Competitive Advantages
Deciding to invest in an emerging market like North Africa requires careful consideration, but the potential benefits the region offers are undeniable. From attractive returns to strategic location and an increasingly improving investment ecosystem, North Africa is becoming an increasingly compelling destination.
High Return Potential in Emerging Markets
One of the main reasons international investors are attracted to North Africa is the potential for higher returns compared to mature economies. Emerging markets often offer more attractive profit margins, especially in sectors undergoing rapid growth.
- Fintech: As mentioned, the financial technology (fintech) sector is booming in many North African countries, particularly Egypt. Demand for digital payment solutions, online lending, and other innovative financial services is skyrocketing, creating ample space for startups and investors.
- Businesses Focused on Sustainability: Global awareness of climate change and the need for sustainable solutions are driving investment in renewable energy, climate-smart agriculture, waste management, and green technology. Countries like Morocco are leading in the solar energy sector, and businesses focused on sustainability often have superior growth potential as consumers and governments increasingly prioritize environmentally friendly products and services.
- Other Growth Sectors: Besides fintech and sustainability, sectors such as e-commerce, digital health, educational technology (edtech), and logistics are also showing impressive growth rates, opening up many opportunities for discerning investors.
Strategic Location and Market Access
North Africa’s geographical location is an invaluable asset. The region serves as a natural bridge, connecting three important continents:
- Europe: Proximity and preferential trade agreements with the European Union (EU) make it easy for manufacturers in North Africa to access the vast European market.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: North Africa is a crucial gateway to the fast-growing markets in sub-Saharan Africa, a region with a young population and enormous economic growth potential.
- Middle East: Close cultural and economic ties with wealthy Middle Eastern countries also open up opportunities for cooperation and investment.
North Africa has a strategic location
This strategic location not only facilitates trade but also gives investors access to a combined market of hundreds of millions of consumers. Furthermore, being situated on major shipping routes, such as the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea, further enhances the region’s appeal for logistics and supply chain activities.
Diverse and Improving Investment Ecosystem
The business environment in North Africa is continuously improving thanks to government reform efforts and increased adoption of digital technology.
- Economic Reforms: Many countries are implementing reforms aimed at simplifying administrative procedures, increasing transparency, protecting intellectual property rights, and improving the legal framework for investment. Special economic zones and free industrial parks with tax incentives and favorable regulations are also being established to attract foreign capital.
- Digital Technology Adoption: The boom in mobile internet and digital solutions is changing the way business is conducted in North Africa. This not only creates new opportunities in the technology sector but also helps improve the operational efficiency of traditional businesses. Digital transformation is making it easier to do business, from marketing and sales to supply chain management and customer service.
- Young Workforce: The region has a young, dynamic, and increasingly well-educated population. This is a critical talent pool for businesses looking to expand their operations.
While each country has its specific characteristics, the general trend is towards an increasingly open, dynamic, and investor-friendly environment for international investors.
Key Sectors for Investment in North Africa: Harnessing Diverse Potential
North Africa is not just a single market but a collection of economies with their own strengths, offering a wide range of attractive investment opportunities across many sectors. From traditional energy to high technology, the region is witnessing significant growth and innovation.
Energy and Natural Resources: Foundation and Green Future
The energy and natural resources sector has long been an economic pillar for many North African countries and continues to be a magnet for large investments.
- Oil and Gas: Countries like Algeria and Libya possess vast reserves of oil and natural gas. Although the world is shifting towards cleaner energy, demand for fossil fuels is expected to remain significant for many years to come. Investing in exploration, extraction, and modernization of oil and gas infrastructure still offers potential returns. The developing industry in Algeria in the energy sector, particularly gas, continues to play a crucial role in ensuring Europe’s energy security.
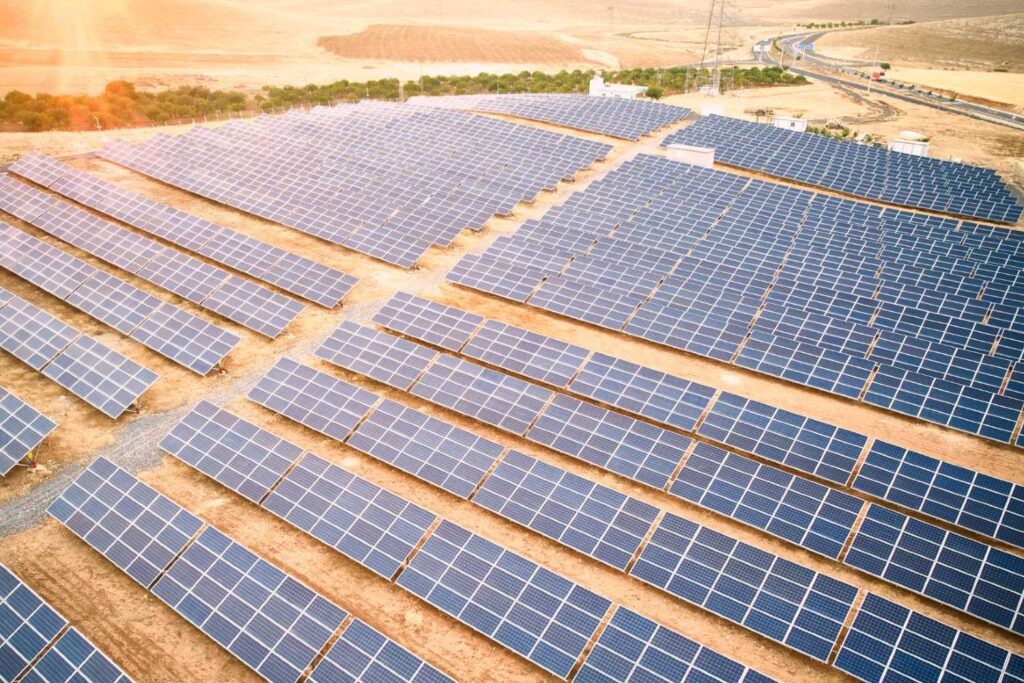

Algeria aims to achieve a renewable energy capacity of 15,000 MW by 2035.
- Renewable Energy: This is a booming growth sector in North Africa. With abundant solar resources (especially in the Sahara Desert) and significant wind potential (along the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts), the region is ideally positioned to become a renewable energy powerhouse. Countries like Morocco and Egypt have set ambitious renewable energy targets and are attracting significant investment in large-scale solar and wind projects. The IMF also emphasized the importance of investing in green energy as a driver for growth in the region.
- Mining: In addition to oil and gas, North Africa is rich in other minerals such as phosphates (Morocco is one of the world’s leading producers), iron ore, zinc, and lead. The increasing global demand for critical minerals for batteries and green technologies also opens up new opportunities in the sustainable mining sector.
Manufacturing and Industry: Building Regional Hubs
North African countries, particularly Morocco and Tunisia, are increasingly emerging as important manufacturing and industrial hubs in the region.
- Competitive Advantages: Factors such as competitive labor costs, geographical proximity to the European market, preferential trade agreements (e.g., with the EU), and increasingly improving infrastructure are attracting multinational companies to set up manufacturing plants here.
- Key Industries:
- Automotive: Morocco has developed a strong automotive industry, attracting major manufacturers like Renault and Stellantis. The country is aiming to increase localization and develop ancillary supply chains.
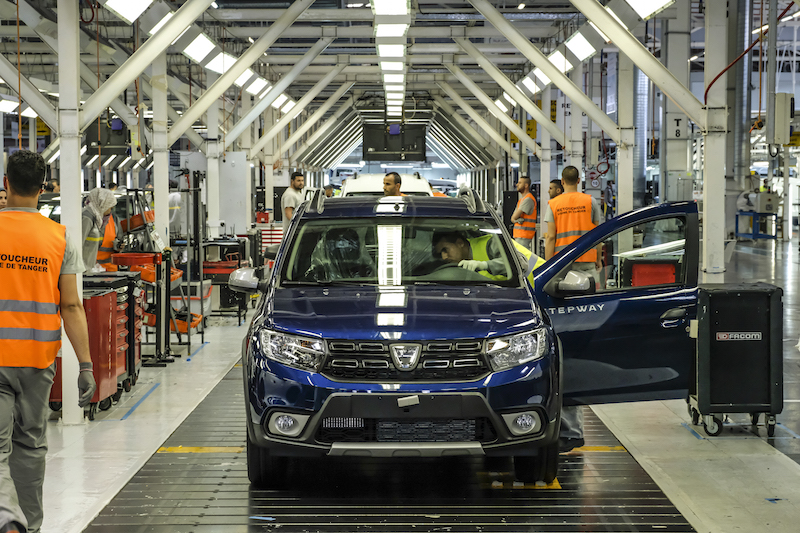

Renault has invested in a factory in Morocco
- Aerospace: Both Morocco and Tunisia have developing aerospace clusters, producing components for major companies like Boeing and Airbus.
- Textiles and Leather Goods: These are traditional sectors but still contribute significantly to exports and employment, especially in Tunisia and Egypt.
- Food and Beverage Processing: With a developed agricultural sector, the potential for the food processing industry to serve domestic and export markets is immense.
- Automotive: Morocco has developed a strong automotive industry, attracting major manufacturers like Renault and Stellantis. The country is aiming to increase localization and develop ancillary supply chains.
- Morocco’s real estate potential in the industrial and logistics sectors is also very significant, as demand for modern factories and warehouses is increasing to support expanding manufacturing and export activities. The development of specialized industrial zones is a testament to this trend.
Agriculture and Agribusiness: Ensuring Food Security and Export Growth
Agriculture is a crucial economic sector, providing livelihoods for a large portion of the population and contributing to food security in the North African region.
- Modernization Opportunities: Despite great potential, agriculture in many areas still relies on traditional methods. This creates significant opportunities for investment in modernization, including water-saving irrigation technology, high-yield crop varieties, agricultural mechanization, and smart agriculture solutions (agritech).
- Value Addition: Instead of just exporting raw agricultural products, there is significant opportunity to invest in agribusiness processing facilities, creating higher value-added products for domestic and export markets. Examples include processing olive oil, dried fruits, canned vegetables, and dairy products.
- Export Growth: High-quality North African agricultural products such as citrus fruits, olives, dates, and vegetables are in high demand on international markets, especially in Europe. Investing in improving quality, packaging, and logistics can help boost export competitiveness.
Tourism and Hospitality: Harnessing Cultural Heritage and Natural Beauty
With rich cultural heritage, world-famous historical sites, and diverse natural beauty, the tourism and hospitality sector is a vital economic pillar and offers many attractive investment opportunities in North Africa, particularly in countries like Egypt, Morocco, and Tunisia.
- Diverse Appeal: From the ancient pyramids of Egypt, the vibrant souks and ancient medinas of Morocco, to the beautiful Mediterranean beaches of Tunisia, North Africa offers a wide range of unique travel experiences.
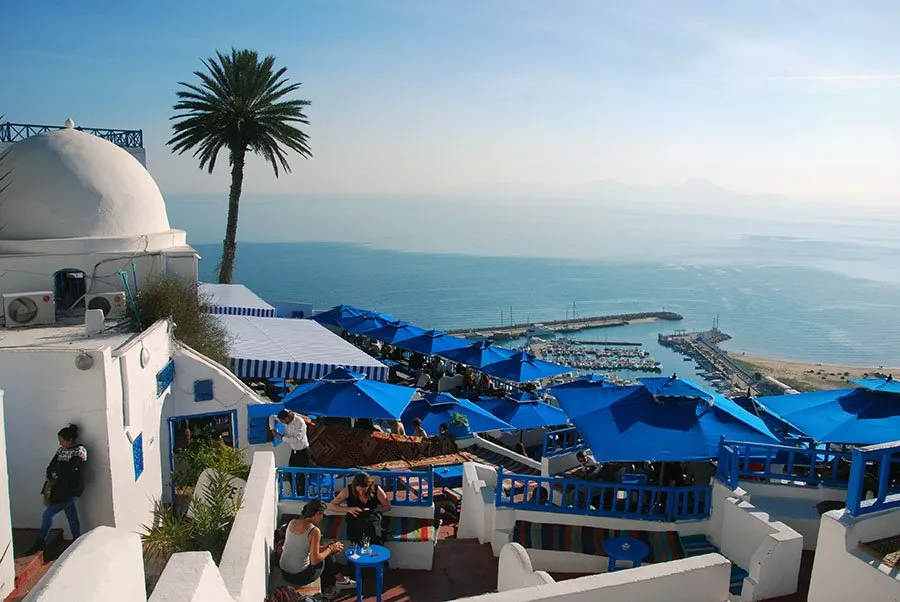

the beautiful Mediterranean beaches of Tunisia
- Investment Opportunities:
- Tourism Infrastructure Development: Including building and upgrading hotels, resorts, restaurants, entertainment centers, and supporting infrastructure like airports and roads.
- Niche Tourism: There is potential to develop niche tourism types such as cultural tourism, ecotourism, adventure tourism, wellness tourism, and MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, Exhibitions) tourism.
- Travel Tech: Investing in online booking platforms, travel guide applications, and other technological solutions to enhance the visitor experience.
- The recovery of the tourism industry after the pandemic is creating new momentum for investment in this sector, with governments actively promoting and attracting international visitors.
Navigating the Investment Process: Key Steps and Considerations
Entering a new market like North Africa requires thorough preparation and a clear strategy. Understanding the process, legal regulations, and key factors for success will help investors minimize risks and maximize opportunities.
Steps to Starting Investment in North Africa
Successful investment often follows a structured path. Here are the main steps investors should consider:
- Conduct Market Research and Due Diligence:
- Identify Target Sectors and Countries: Based on your investment goals, risk appetite, and expertise, pinpoint specific sectors and countries in North Africa that interest you.
- Analyze the Market: Assess market size, growth potential, competitors, consumer behavior, and macroeconomic factors that could impact your investment.
- Legal and Financial Due Diligence: Thoroughly examine the financial situation, ownership structure, reputation, and potential legal issues of any target partners or companies.
- Identify and Partner with Local Partners or Advisors:
- Importance of Local Knowledge: Local partners (such as distributors, suppliers, or joint venture partners) can provide invaluable insights into the market, local networks, and business culture.
- Professional Advisors: Engage legal, financial, and business consulting firms with experience in the target market for support on legal, tax, and market entry strategy aspects.
- Comply with Local Regulations and Establish a Legal Entity:
- Business Registration: Understand the requirements for business registration, different types of companies (e.g., limited liability company, joint-stock company), and the establishment process.
- Licenses and Approvals: Identify the specific business licenses, industry-specific permits, and necessary approvals from government agencies. This process can vary significantly between countries and sectors.
- Leverage Investment Incentives and Free Economic Zone Regulations (if applicable):
- Government Incentives: Many North African countries offer investment incentives such as tax exemptions or reductions, subsidies, and other favorable conditions to attract foreign direct investment, especially in priority sectors.
- Free Zones: These zones often provide preferential legal and tax regimes, simplified customs procedures, and better infrastructure. Research whether locating your headquarters or operations in a free zone is suitable for your business model.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
The legal and regulatory environment in North Africa can be complex and varies significantly between countries.
- Specific Investment Laws: Each country has its own investment law, regulating the rights and obligations of foreign investors, restricted investment sectors, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Company Registration Requirements: The process, required documents, and timeline for company registration can differ.
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Sectors such as banking, telecommunications, energy, and pharmaceuticals often have their own specific regulations and regulatory bodies.
Importantly, as iHub Kenya emphasizes, investors should seek advice from local legal experts to effectively navigate these legal frameworks and avoid common pitfalls. Non-compliance can lead to delays, penalties, or even inability to operate.
Advice for Successful Market Entry
In addition to complying with formal procedures, several practical strategies can help increase your chances of success:
- Start with small, scalable projects to test the market: Instead of committing a large investment initially, consider starting with a pilot project or a smaller-scale operation. This allows you to better understand the market, test your assumptions, and adjust your strategy before scaling up.
- Focus on sectors aligned with national development priorities: Projects that align with the host government’s socio-economic development plans are often more likely to receive support and incentives. For example, projects in renewable energy, digital technology, job creation, or infrastructure development are generally welcomed.
- Build relationships with government agencies and local stakeholders: Good relationships with state regulatory bodies, industry associations, and local communities can help resolve issues more smoothly and build credibility for your business. Patience and cultural understanding are key to building sustainable relationships.
- Cultural understanding and adaptation: Cultural differences can affect every aspect of business, from negotiation and human resource management to marketing. Investing time to understand and respect the local culture will help you build trust and avoid misunderstandings.
Case Studies: Successful Investments in North Africa and Investment Opportunities in Egypt
Theory and planning are important, but real-world examples of success (and failures) can provide valuable lessons for potential investors. North Africa has witnessed many success stories across diverse sectors, demonstrating the region’s significant potential when strategies are executed correctly.
Examples of Companies That Have Thrived in the Region
- Fintech Growth in Egypt – A Testament to Investment Opportunities in Egypt:
Egypt has emerged as a vibrant fintech hub in the Middle East and Africa. This dynamism is driven by a young, tech-savvy population, high smartphone penetration, and government support for promoting cashless payments. The rapid development of digital infrastructure has attracted significant venture capital, with several startups scaling up to become regional leaders.- Fawry: One of the most prominent success stories is Fawry, a leading Egyptian electronic payment platform. The company offers a range of payment services, from utility bills and mobile top-ups to booking tickets and online payments. Fawry has successfully listed on the Egyptian Stock Exchange and continues to expand its services.
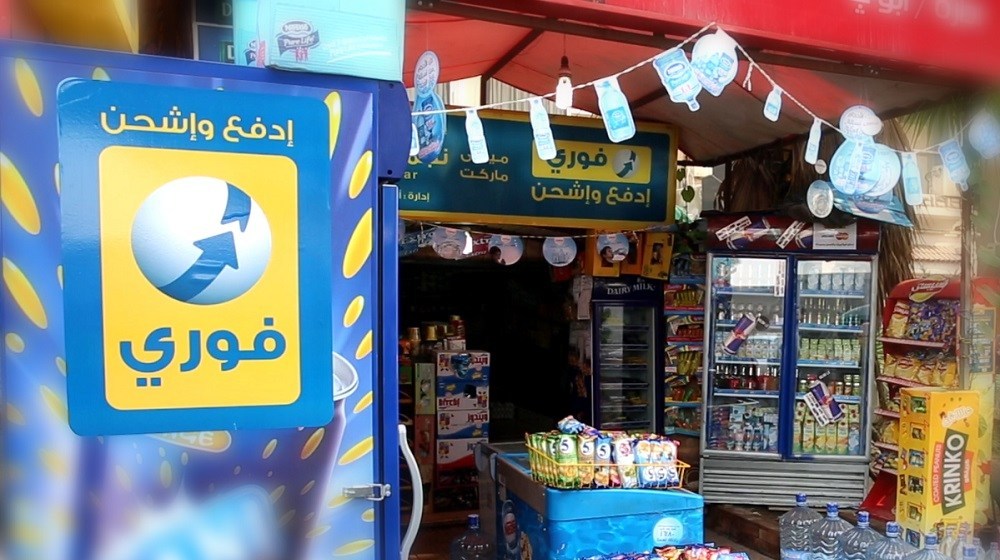

Egypt’s Fawry is currently a multi-billion dollar company
- P2P Lending and Digital Microfinance Market: Startups in the peer-to-peer (P2P) lending space and providing digital microfinance solutions are also gaining traction, addressing the credit access needs of individuals and small businesses underserved by traditional banks. Investment opportunities in Egypt within the fintech sector remain vast, particularly in segments like insurtech and digital asset management.
- Fawry: One of the most prominent success stories is Fawry, a leading Egyptian electronic payment platform. The company offers a range of payment services, from utility bills and mobile top-ups to booking tickets and online payments. Fawry has successfully listed on the Egyptian Stock Exchange and continues to expand its services.
- Renewable Energy in Morocco – Leveraged by Morocco’s Real Estate Potential:
Morocco has set ambitious renewable energy targets, aiming to generate over 52% of its electricity capacity from renewable sources by 2030. Strong government support, a clear regulatory framework, and large-scale solar projects have attracted international investors and set global standards for green investment in Africa.- Noor Ouarzazate Project: This is one of the world’s largest concentrated solar power (CSP) plants, a testament to Morocco’s commitment to clean energy. The project not only supplies electricity to millions but also creates jobs and promotes technology development.
- Private Investment: Many international energy companies have invested in wind and solar power projects in Morocco, attracted by resource potential and the stability of the investment environment.
- Morocco’s real estate potential also indirectly benefits, as large energy projects require significant land area and supporting infrastructure. Furthermore, the development of clean energy enhances the country’s image and attracts other industries interested in sustainability, which in turn can boost demand for industrial and commercial real estate. Morocco’s success in the renewable energy sector has become a model for other countries in the region.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
From success stories and challenges faced by investors, several important lessons and best practices can be drawn:
- Adapt the business model to the local context:
- There is no “one size fits all” solution. What works effectively in one market may not be suitable in another. It is crucial to understand the needs, preferences, and culture of local consumers to adapt products, services, and marketing strategies accordingly.
- For example, in the fintech sector, products need to be designed to address specific needs of local users, such as the demand for Cash on Delivery (COD) payment options or Sharia-compliant financial solutions.
- Invest in local talent and continuously engage with stakeholders:
- Recruiting and developing local talent not only helps the business better understand the market but also demonstrates commitment to the community.
- Maintaining open and regular dialogue with government agencies, business partners, customers, and the local community is vital for building trust, proactively addressing issues, and ensuring sustainable business operations.
- Prioritize sustainability and innovation for long-term success:
- Businesses that focus on environmentally and socially sustainable practices often have a long-term competitive advantage. This is increasingly important as consumers and investors become more concerned with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) issues.
- Continuous innovation is key to remaining relevant and competitive in a dynamic market. This includes adopting new technologies, developing new products and services, and improving operational processes.
These case studies show that with the right strategy, deep market understanding, and adaptability, investors can achieve significant success in North Africa.
Risks and Challenges: Navigating a Complex Terrain
While North Africa offers many attractive opportunities, investors also need to be clearly aware of the potential risks and challenges. Understanding and preparing for these factors is crucial to mitigating negative impacts and ensuring the sustainable success of investment projects.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Some common mistakes investors might make when entering the North African market include:
- Overestimating market size or growth rate:
- Pitfall: Relying on unfounded optimistic assumptions or not fully understanding the actual purchasing power of consumers.
- How to avoid: Conduct thorough market research, use multiple data sources, and consider socio-economic factors that can influence demand. Start small and expand gradually when there is evidence of market acceptance.
- Underestimating the complexity of regulations and bureaucracy:
- Pitfall: Assuming processes will be similar to those in the home market or other developed markets. Delays in obtaining licenses, unclear or sudden changes in legal requirements can cause significant problems.
- How to avoid: Seek professional legal advice from reputable local law firms from an early stage. Build good relationships with government agencies and be patient with administrative processes.
- Inadequate risk assessment:
- Pitfall: Overlooking or downplaying specific political, economic, social, or operational risks of the region or country.
- How to avoid: Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment, including worst-case scenarios. Develop contingency plans and risk mitigation strategies.
Political and Economic Risks
These are critical factors that investors need to monitor closely:
- Policy changes and political instability:
- Government policies can change, sometimes abruptly, affecting the investment environment, tax rates, or industry regulations.
- Political instability, although reduced in some areas, can still be a factor in some countries, leading to uncertainty and business disruption. The World Bank regularly updates on macroeconomic risks that investors should consult.
- Currency fluctuations:
- The local currencies of some North African countries can fluctuate significantly against major currencies like USD or EUR. This can affect returns when repatriating profits and import costs.
- Capital controls or restrictions on profit repatriation can also be a risk in some markets.
- Regional conflicts and spillover effects:
- Although not all North African countries are directly affected, conflicts in neighboring regions or within the MENA region itself can have spillover effects on investor confidence, supply chains, and tourism flows. The IMF has also noted the impact of geopolitical factors on the region’s economic outlook.
- Inflation and cost pressures:
- High inflation rates in some countries can erode purchasing power and increase operating costs.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
While it is impossible to eliminate risks entirely, investors can adopt strategies to manage and mitigate their impact:
- Diversify investments:
- Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. If possible, consider diversifying investments across multiple countries or sectors within the North African region to reduce reliance on a single market or industry.
- Use political risk insurance:
- Organizations like the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) of the World Bank Group and private insurance companies offer political risk insurance products. These products can protect against risks such as expropriation, war and civil disturbance, and breach of contract by the government.
- Partner with reliable local partners:
- A strong, reputable local partner with deep market knowledge can help navigate regulatory, cultural, and operational challenges. They can also provide early warnings of potential changes in the business environment.
- Conduct continuous due diligence and closely monitor the business environment:
- The business environment is not static. Investors need to continuously monitor macroeconomic trends, political developments, and changes in the legal framework. Maintain flexibility to adjust strategies as needed.
- Structure investments carefully:
- Consider using bilateral investment treaties (BITs) or free trade agreements (FTAs) which may provide additional protection for investors. Consult with legal experts on how to structure the investment to optimize protection and tax benefits.
By proactively identifying and addressing these risks, investors can significantly improve their chances of success and contribute to the sustainable development of the North African region.
Future Outlook for North African Investment and the Developing Industry in Algeria
Looking ahead, the investment landscape in North Africa is projected to become increasingly vibrant and attractive. Many factors are converging to drive growth and open up new opportunities, although challenges still need to be managed carefully.
Predictions for Market Growth and Development
The economic outlook for North Africa in the coming years is generally positive, supported by several key drivers:
- Oil Production Recovery and Growth: For oil and gas producing countries like Algeria and Libya, the recovery in oil prices and potential for increased production (if conditions stabilize) will be a significant growth driver. This not only brings export revenue but can also stimulate investment in related sectors.
- Deep Digital Transformation: The adoption of digital technology is accelerating across the region, from e-government, fintech, and e-commerce to Industry 4.0 solutions. This digital transformation is identified by S&P Global Market Intelligence as one of the key themes for the MENA region in 2025, promising to boost productivity, create new business models, and attract investment in the technology sector.
- Green and Sustainable Economy: The region’s commitment to renewable energy and sustainable development goals is creating a new wave of investment. The IMF also emphasizes the role of the green economy in driving more diversified and sustainable growth for North Africa. Projects in solar power, wind power, green hydrogen, and climate technology (climate tech) are expected to attract significant capital.

climate tech is expected to attract significant capital
- Continued Structural Reforms: Many North African governments recognize the need to continue economic reforms to improve the business environment, attract foreign investment, and boost the private sector. Efforts to simplify administrative procedures, increase transparency, and improve governance will play a crucial role.
- Regional and International Integration: Increased economic cooperation within North Africa and with major international partners (such as the EU, China, and Gulf countries) can open up new markets and boost trade and investment flows.
Emerging Opportunities and Sectors to Watch
In addition to traditional sectors, several emerging industries and opportunities are gaining attention and promise significant future growth potential:
- Agricultural Technology (Agri-tech): With the need to ensure food security and cope with climate change, investment in technological solutions for agriculture (such as precision farming, smart irrigation, drought-resistant crop varieties, and digital agricultural supply chains) is becoming increasingly important.

Agricultural technology in North Africa is full of potential
- Climate Technology (Climate Tech): Encompasses a range of innovative solutions aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change and adapting to unavoidable changes. This includes renewable energy, energy storage, carbon capture, sustainable water management, and green materials.
- Infrastructure Development: The need for modern infrastructure (transport, logistics, energy, water, and telecommunications) remains significant in many parts of North Africa. Public-Private Partnership (PPP) projects can offer attractive opportunities for long-term investors.
- Logistics and Supply Chains: With its strategic location, North Africa has the potential to become a key logistics hub. Investment in ports, warehouses, multimodal transport, and digital logistics solutions will be essential to support trade growth.
- Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Industry: Growing demand for healthcare, coupled with government efforts to reduce reliance on imported medicines and medical equipment, is creating opportunities for domestic pharmaceutical manufacturing and the development of high-quality healthcare services. The developing industry in Algeria, for example, is making strides in localizing pharmaceutical production.
- Education and Skills Training: The region’s young population requires investment in education and vocational training to equip them with the skills needed for the future labor market, especially in technology and engineering fields.
According to iHub Kenya’s assessment, these sectors, along with the continuous development of digital technology and the green economy, will shape North Africa’s investment landscape in the coming years. Investors with foresight and the ability to seize these emerging trends will be well-positioned for success.
Conclusion
Investing in the North African market clearly presents an attractive picture for global investors seeking high growth opportunities and portfolio diversification. From increasing economic dynamism, a strategic geographical location connecting continents, to significant untapped potential in key sectors like energy, manufacturing, agriculture, tourism, and technology, North Africa is truly a promising land.
Together, we have explored the region’s competitive advantages, reviewed key markets like Egypt with its booming fintech ecosystem, Morocco with its strong progress in renewable energy and industry, and Algeria with its abundant energy resources and economic diversification efforts. However, every investment journey comes with challenges. Understanding and preparing for political and economic risks, and the complexity of the legal environment, are prerequisites for success.
With thorough due diligence, building solid partnerships with local entities, and an effective risk management strategy, investors can fully harness the significant benefits from North Africa’s expanding markets, resource wealth, and strategic location. The region offers not only financial return potential but also an opportunity to contribute to the sustainable socio-economic development of one of the world’s most dynamic regions.
To realize these opportunities, we encourage interested investors to begin their journey of discovery. Delve deeper, consult with local experts and experienced consulting firms, and stay updated on the latest developments in the region. With meticulous preparation and a strategic vision, investing in North Africa can yield optimal results and contribute to the region’s impressive growth story in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is 2025 considered a golden time to invest in the North African market?
2025 marks a period where many favorable factors converge: economic recovery after global fluctuations, strong reform policies from governments, acceleration in digital transformation, and commitment to sustainable development. Positive GDP growth forecasts, coupled with untapped potential and the need for portfolio diversification by international investors, make North Africa an attractive destination.
2. Which sectors have the greatest investment potential in North Africa?
Sectors with great potential include: Energy (both oil and gas, and renewable energy, especially solar and wind), Manufacturing (automotive, aerospace, textiles, food processing), Agriculture and Agribusiness (modernization, value addition), Tourism and Hospitality, and Technology (Fintech, e-commerce, Edtech). Emerging sectors like Agri-tech and Climate-tech are also very promising.
3. What are the main risks when investing in North Africa and how to mitigate them?
Key risks include political instability and policy changes, currency fluctuations, complexity of regulations and bureaucracy, and impacts from regional conflicts. To mitigate, investors should: conduct thorough due diligence, diversify investments, use political risk insurance, partner with reliable local partners, and closely monitor the business environment.
4. What are the notable investment opportunities in Egypt?
Egypt stands out with its large consumer market and booming fintech ecosystem. Notable investment opportunities focus on financial technology (Fawry is a successful example), digital payments, and P2P lending. Additionally, large infrastructure projects like the Suez Canal Economic Zone, manufacturing, and tourism also offer significant potential.
5. What is the future outlook for investment in North Africa?
The future outlook is very positive and dynamic. The push for digital transformation, commitment to the green and sustainable economy, along with ongoing structural reforms, will create many new opportunities. Sectors like agricultural technology (agri-tech), climate technology (climate-tech), infrastructure development, logistics, and the pharmaceutical industry are projected to grow strongly, attracting more investment and contributing to the region’s overall development.

