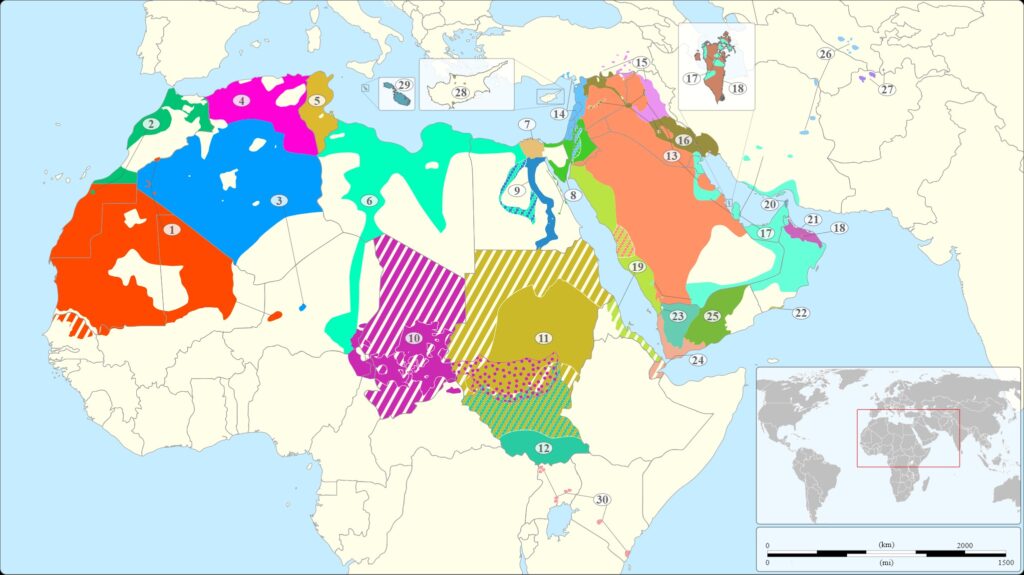
With more than 420 million native speakers worldwide, Arabic is one of the most widely spoken languages and is officially used in 28 countries. As an important language in literature, commerce, and business, Arabic has a large number of speakers globally.
Thanks to its development over time, Arabic has produced many different dialects. Although Arabic is primarily divided into three main forms: Classical Arabic (or the Arabic in the Quran), Modern Standard Arabic, and everyday colloquial Arabic, there are actually more than 25 Arabic dialects used around the world. You can refer to the list of the ten countries using the most popular Arabic dialects below and see the full list in the article How many countries speak Arabic in the world?
| No | Country | Population | No. of Arabic Speakers |
| 1 | Egypt | 100,000,000 | 82,449,200 |
| 2 | Algeria | 41,701,000 | 40,100,000 |
| 3 | Sudan | 40,235,000 | 28,164,500 |
| 4 | Iraq | 36,004,552 | 22,908,120 |
| 5 | Morocco | 35,250,000 | 25,003,930 |
| 6 | Saudi Arabia | 30,770,375 | 27,178,770 |
| 7 | Yemen | 23,833,000 | 14,671,000 |
| 8 | Syria | 20,956,000 | 17,951,639 |
| 9 | Tunisia | 10,982,754 | 10,800,500 |
| 10 | Somalia | 10,428,043 | 3,788,000 |
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA)
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is the most popular and widely used form of Arabic, as it is shared and known by Arabic speakers around the world. MSA is also taught in universities and used in important fields such as communication, commerce, and business. It serves as the main language in literature, technology, medicine, and education, but is not used in everyday situations. Although MSA is a standard dialect for many Arabic speakers, pronunciation differences are one of the most confusing factors. Because Modern Standard Arabic is widely used, each speaker may have a different pronunciation depending on region and background, which means it will take time to get used to the accents, dialects, and differences in pronunciation.
See more: Is it worth learning Arabic and where to learn Arabic
1- Egyptian Arabic
The Egyptian dialect is primarily spoken in Egypt and is one of the most popular Arabic dialects. This dialect appears in television shows and movies, and because it is widely used in the Arabic-speaking community, it is the most easily understood dialect. Notably, Egyptian dialect is influenced by many other languages such as French, Greek, Turkish, English, and Italian, reflecting its rich diversity and origins, even though it is written in the Arabic script. This dialect also attracts many new learners because it is accessible and has a wealth of learning resources.

2- Maghrebi Arabic
Maghrebi dialect has over 70 million speakers and is one of the most popular Arabic dialects. What makes Maghrebi special is the diversity in its speech. Those who speak Maghrebi often refer to their language as Derja, Derija, or Darija (الدارجة), meaning “progress and development”. This name reflects the development and spread of Maghrebi. The language is constantly evolving and integrating with French and Italian, especially in technical fields, and also incorporates vocabulary from Modern Standard Arabic (MSA). Therefore, Maghrebi or Derja truly lives up to its name.
3- Gulf Arabic
The Gulf dialect has around 36 million speakers across the Arab world. It is primarily used in the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait, and some regions of Saudi Arabia such as Oman and Iraq. However, this dialect differs in pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary because it is truly a collection of similar dialects. Therefore, you will notice sharp differences, especially with dialects that are geographically far apart, such as the differences between the Qatari and Kuwaiti dialects. As a result, even if you know one dialect, you may still have difficulties understanding someone speaking a different dialect. However, that is the exciting aspect of language, showcasing its flexibility and diversity.
4- Levantine Arabic
The Levantine dialect has over 21 million speakers and is commonly used in daily communication as well as in writing. Levantine speakers still use Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) in formal situations. This dialect is popular in Syria, Jordan, Palestine, and Lebanon, and is the second most popular dialect in media and films, after the Egyptian dialect. Levantine has a significant history dating back to the 7th century, when it emerged from the transition from Aramaic to Arabic. For Arabic learners, Levantine is an interesting option as it has close ties to ancient languages.
To better understand the differences among these dialects, you can refer to the examples and videos below to see the pronunciation and vocabulary differences between them.
| ENG | MSA | LEV | GLF |
| book | ktAb | ktAb | ktAb |
| money | nqwd | mSAry | flws |
| Come on! | hyA! | ylA! | ylA! |
| ENG | GLF | EGYP | MAGH | LEV |
| magic | siħir | siħir | siħir | siħir |
| corruption | fasa:d | fasa:d | fasad | fasa:d |
| day | Yo:m | Yo:m | Yum or nhar | Yo:m |
| ENG | MSA | EGYP | LEV |
| What time is it? | kam as-saعah كَمْ السَّاعَة؟ |
issahعa kaam اِسَّاعَة كَام؟ |
kam assaعah كَمْ اسَّاعَة؟ |
| How are you? | kayf anta كَيْف أَنْتَ؟ |
إِزَّايَك؟ izzayyak | kiifak كِيْفَك؟ |
| What are you doing? | mathaa tafعal مَاذَا تَفْعَل؟ |
bi-tiعmal eeh بِتِعْمَل إِيْه؟ |
shuu عam tiعmal شُوْ عَم تِعْمَل؟ |
Do you have complex text that needs to be translated into one of these dialects? Please contact Nuhaira, they might be able to help you!