What Is Haram? Exploring a Crucial Concept in Islamic Life
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
- Haram means “absolutely forbidden” in Islam, covering actions, food, and drinks.
- Understanding haram is very important for living harmoniously in a multicultural environment.
- This article will delve into the definition, meaning, examples, origin, and impact of haram on the lives of Muslim followers.
- Detailed Definition: What Is Haram?
- Meaning and Distinction of Related Terms: Haram, Halal, Makruh
- Practical Examples of Haram
- Origin and Religious Context of Haram
- Impact of Haram on the Lives of Muslim Followers
- Common Areas Considered Haram
- Consequences of Violation and Benefits of Adherence to Haram
- Comparison of Haram with Related Concepts (Halal, Makruh, etc.)
- Frequently Asked Questions About What Haram Is – Notes for Non-Muslims
- Conclusion: Summary and Recommendations
Detailed Definition: What Is Haram?
To fully answer the question of what haram is, we need to delve into the roots of this term. In Arabic, haram (حَرَام) means “forbidden,” “not permitted,” or “unlawful” according to Islamic regulations. The word originates from the verb “harama,” which means “to forbid” or “to prohibit’
In the religious context of Islam, haram is anything that is absolutely forbidden by Allah (God). Anyone who intentionally violates haram rules will be held accountable and may face punishment, whether in this world or on the final Day of Judgment. This is an absolute concept with no exceptions, and believers must completely avoid it to maintain both physical and spiritual purity.
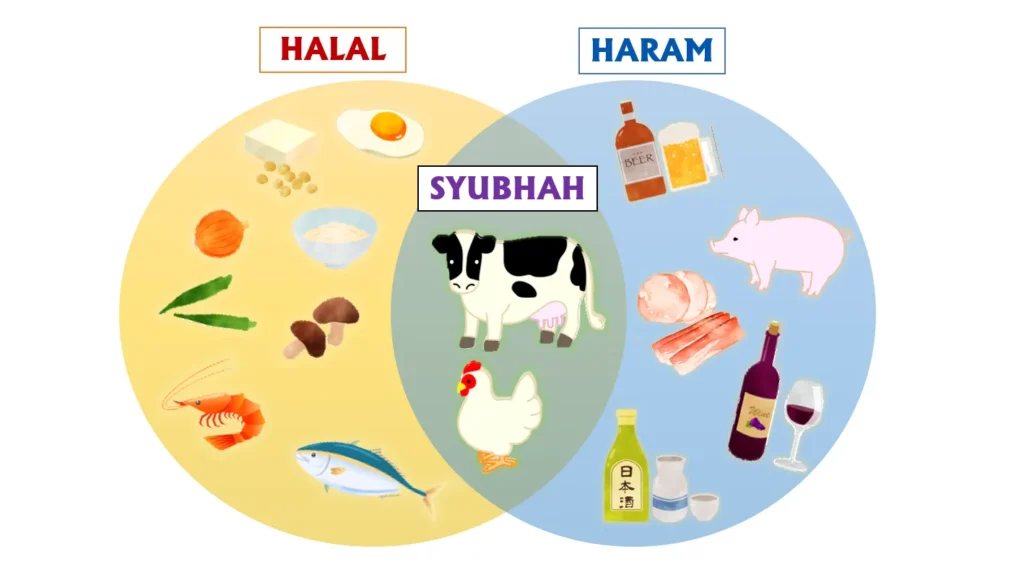
Meaning and Distinction of Related Terms: Haram, Halal, Makruh
In Islam, there is a very detailed system for classifying actions and materials, helping believers clearly identify what should be done and what should be avoided. To better understand what haram is, we need to distinguish it from other important terms:
- Halal: This term means “permissible,” “lawful,” or “in accordance with Islamic standards.” These are things that believers are encouraged to do or use.
- Haram: As analyzed, these are things that are “absolutely forbidden” in Islam, which must be completely avoided in all forms.
- Makruh: The concept of makruh (مَكْرُوه) refers to things that are “discouraged” or “not recommended,” but not absolutely forbidden. Although not haram, avoiding makruh is considered a good deed, helping believers strive for greater perfection.
Comparison Table of Function and Level of Prohibition
| Term | Basic Definition | Level of Prohibition | Consequences of Violation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Halal | Permissible, lawful | Not forbidden | None |
| Haram | Absolutely forbidden | Completely forbidden | Punishable (religious/legal) |
| Makruh | Discouraged, not recommended | Not absolutely forbidden | No direct punishment, but not good |
Clearly distinguishing between haram, halal, and makruh is extremely important. It helps Muslims make the right decisions in their daily lives, and at the same time, helps non-Muslims understand and respect the customs of the Muslim community, avoiding unnecessary misunderstandings when communicating or working together.
Practical Examples of Haram
To get a clearer picture of what haram is in daily life, let’s look at some common examples of things that are absolutely forbidden:
- Food:
- Pork and pork products: This is the most famous example of haram food.
- Dog meat: Also forbidden to eat in Islam.
- Blood and blood products: Any type of blood is forbidden for consumption.
- Meat of animals not slaughtered according to ritual (carrion): Animals not slaughtered in the halal way (by cutting the throat and reciting Bismillah) are considered haram.
- Amphibians and some venomous species: Such as frogs, snakes.
- Animals with sharp claws and fangs: Such as lions, tigers, bears, along with birds of prey like eagles.
- Drinks:
- Alcohol, beer, and all alcoholic beverages: Any drink that causes intoxication is absolutely forbidden
- Actions:
- Gambling: All forms of gambling are haram.
- Usury (Riba): The practice of lending money at exorbitant interest rates or exploiting others in financial transactions is forbidden.
- Fraud, deception: In business, studies, or any aspect of life.
- Adultery, sexual relations outside of marriage: Strictly forbidden and considered a major sin.
- Theft, robbery: Acts that violate others’ property
- Lifestyle:
- Practicing superstitions: Believing in fortune-telling, charms, or anything that contradicts the belief in the one Allah.
- Consuming immoral cultural products: Including films, books, music with pornographic or violent content, or that encourages haram behavior.
- Excessively luxurious or wasteful lifestyle: Although not absolutely forbidden, wastefulness and extravagant spending are often considered makruh or even haram if they exceed permissible limits.
These examples help us understand that haram is not limited to food but covers many aspects of life, shaping the behavior and choices of Muslim followers.

Origin and Religious Context of Haram
The concept of haram is not an arbitrary rule but is based on the most important sources of law in Islam: the Qur’an and the Hadith. They are the guiding principles for all aspects of a believer’s life.
- The Qur’an: It is the holy scripture of Islam, believed to be the direct revelation of Allah to the Prophet Muhammad. The Qur’an clearly states the basic regulations about haram, such as the prohibition of eating pork, drinking alcohol, and engaging in gambling. The verses in the Qur’an are the foundation for all laws regarding haram.
- The Hadith: This is a collection of the teachings, actions, and approvals of the Prophet Muhammad. The Hadith serves to supplement and explain in detail the regulations in the Qur’an, guiding how to apply haram in the practical religious life in a specific and clear manner. For example, the Hadith may detail the halal slaughtering process or which specific actions are considered riba.
The rules of haram are established to preserve the purity, morality, and health of the community of believers, helping them live a meaningful life in compliance with Allah’s will.
Impact of Haram on the Lives of Muslim Followers
The regulations on haram are not just a list of prohibitions; they profoundly shape the lifestyle and choices of every Muslim follower. Adhering to haram
becomes an indispensable part of daily life, from the smallest matters to major decisions.
- Guiding Personal Choices: Haram regulations directly influence the choice of food, drink, clothing, recreational activities, and even career or financial investments. Believers must ensure that all aspects of their lives comply with Islamic principles, staying away from what is forbidden. This helps them live a disciplined and purposeful life.
- Maintaining Morality and Purity: By staying away from haram things, believers are guided to maintain a clear conscience, avoiding bad behaviors such as lying, cheating, stealing, or extramarital relations. This contributes to building a moral individual who is responsible for themselves and the community.
- Strengthening Community Values and Unity: The common rules of haram help create a solid moral framework for the entire Muslim community. When all members adhere to the commandments, unity and mutual trust are strengthened. This also helps to limit social evils and protect the general health of the community, for example, the prohibition of alcohol helps reduce health and social problems related to substance abuse. As a result, an Islamic society often values purity, equality, and mutual support.
Thus, haram is not just about what is forbidden, but is also a tool for character development, building a healthy society, and preserving religious identity.
Common Areas Considered Haram
To give you a more comprehensive view, let’s go over the main areas where haram regulations frequently appear:
- Food & Drink:
- Pork: This meat is completely forbidden as it is considered unclean from an Islamic perspective.
- Alcohol and intoxicants: Any drink or substance that impairs consciousness or is addictive is forbidden to protect the reason and health of believers.
- Blood, animals that die naturally or are not slaughtered according to the Islamic method (Dhabiha): These are forbidden to ensure hygiene and respect for life.
- Personal Behavior:
- Gambling: Forbidden because it is considered a form of fraud, is addictive, and destructive to personal and family finances.
- Riba (Interest/Usury): Lending money at excessive interest rates or exploitation in financial transactions is forbidden, to encourage fairness and risk-sharing.
- Fraud, Theft, Deception: All dishonest acts in any field are haram, aiming to build a just and honest society
- Zina (Adultery, Sexual relations outside of marriage): Absolutely forbidden to protect the family, the sanctity of marriage, and social morality.
- Lifestyle and Entertainment:
- Art and cultural products that are pornographic or violent: Any content that stimulates base desires or encourages violence is haram.
- Practicing magic, fortune-telling, superstitions: Contradicts the belief in the one Allah.
- Wastefulness, excessive luxury: Although not always absolutely haram, a lifestyle of waste and flaunting wealth is considered contrary to the spirit of humility and thrift in Islam.
These regulations are not just rules but a comprehensive moral system that helps Muslims live a meaningful, ethical life aimed at pleasing God.

Consequences of Violation and Benefits of Adherence to Haram
Adhering to the prohibitions of haram is not only a religious duty but also brings clear impacts on personal and community life.
Consequences of violation:
- Religious Sanctions: For Muslim believers, violating haram prohibitions can lead to punishment in the afterlife, also known as the Day of Judgment. The violator will be held accountable before Allah for their actions.
- Islamic Law (): In some countries applying Sharia Law, violating haram can be dealt with by strict legal sanctions, ranging from fines to physical punishments depending on the severity of the act.
- Social Consequences: Violating haram can lead to a loss of reputation, being ostracized by the community, and negatively affecting personal and family honor.

Sharia law
Benefits of adherence:
- Maintaining a clear conscience: Believers feel at peace and secure knowing they are following the path guided by Allah.
- Respected by the community: Adherence demonstrates piety and morality, helping the individual to be respected within the Muslim community.
- Building trust in a just and moral society: When everyone adheres to moral values, society becomes healthier, more just, and more trustworthy, contributing to the reduction of crime and social ills.
- Protecting health and well-being: Abstaining from harmful substances like alcohol and unclean meat helps protect physical health. Avoiding gambling and usury also protects finances and family stability.
It can be seen that adhering to haram is an indispensable part for Muslims to achieve peace of mind and contribute to building a strong, moral community.
Comparison of Haram with Related Concepts (Halal, Makruh, etc.)
To reinforce the knowledge of what haram is and its related terms, let’s review a summary comparison table, highlighting the core differences:
| Criteria | Haram | Halal | Makruh |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Absolutely forbidden | Permissible, lawful | Discouraged, not recommended |
| Level | Most severe, intolerable | Completely acceptable | Not forbidden but should not be done |
| Origin | From the Qur’an and Hadith (explicitly forbidden) | From the Qur’an and Hadith (explicitly permitted) | From Hadith (discouraged) |
| Consequences | Punishment (religious/legal) | None | No punishment, but misses a reward |
| Example | Pork, alcohol, gambling | Halal-slaughtered beef, plain water, honest business | Smoking, oversleeping, excessive idle talk |
Clearly distinguishing these terms is essential. For Muslims, it helps them make the right choices in all aspects of life. For non-Muslims, especially when living or working in a multicultural environment like Vietnam, understanding the differences between haram, halal, and makruh shows deep respect for the beliefs and customs of Muslims. This understanding will help you avoid awkward situations due to a lack of knowledge, building better and more harmonious relationships.
Frequently Asked Questions About What Haram Is – Notes for Non-Muslims
To conclude our journey of discovering what haram is, Nuhaira would like to answer some frequently asked questions and share some important notes for those who are not Muslim but frequently interact with this community:
- Should products of unknown origin be avoided?
- For Muslims, any product without a clear halal certification or suspected of containing haram ingredients (e.g., pork-based gelatin, alcohol in food/cosmetics) should be carefully checked or, preferably, avoided. The principle is “when in doubt, abstain”.
- Are non-Muslims required to follow haram laws?
- No, haram laws apply directly only to Muslim followers. Non-Muslims are not bound by these rules. However, when communicating, doing business, or living with Muslims, understanding and respecting their rules is a sign of civility and facilitates a harmonious environment.
- In Vietnam and other multicultural countries, what should be noted when interacting or cooperating with Muslims?
- Regarding food: Always be mindful of haram foods like pork and alcohol. When inviting them to a meal, ensure the dishes are halal or ask clearly about the ingredients. Halal restaurants are a safe choice.
- Regarding drinks: Avoid offering alcohol.
- Regarding behavior: Respect their prayer times, and dress modestly when visiting their sacred places.
- In business: Avoid activities related to gambling or usury. Understand that for Muslims, honesty and transparency are paramount in all transactions.
- Communication: Always show an open attitude and respect for their culture and beliefs.
Respecting religious customs not only helps you integrate better but also builds sustainable relationships based on understanding and trust Vatfi.org.vn. That is the key to a diverse and harmonious society.
Conclusion
Through this journey of exploration, we have clarified the concept of what haram is – a core and foundational term in Islamic ethics and social life. Haram is not just about what is forbidden, but it is also an integral part that shapes the identity, lifestyle, and deep moral values of the Muslim community worldwide. From food to personal behavior, from finance to lifestyle, haram regulations guide believers to live a pure, responsible life that is closer to God.
Understanding and respecting haram not only helps you, whether you are a believer or a non-believer, to maintain harmony in social relationships but also contributes to building a healthy society.
See more:
What is a Caliphate? Definition, History & Role in Islam
What is the Middle East? Concept, Scope, and Important Global Role
Discovering the Hijab: A Cultural and Religious Symbol of Muslim Women