What is the Levant? Explore the Countries of the Levant and its Historical, Cultural Significance
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Key points
- Levant is a historically and culturally important region in the Eastern Mediterranean.
- This region includes countries such as Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, and Palestine.
- The Levant has a rich cultural heritage, serving as a center for many ancient civilizations.
- The geographical location of the Levant has shaped its role in history and trade.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to What is the Levant and the Countries of the Levant
- What is the Concept of the Levant? History of the Levant and its Boundaries
- Countries of the Levant and the Levant in Culture and Archaeology
- Geographical Significance of the Levant and its Boundaries
- Culture and Heritage of the Levant in Culture and Archaeology
- Influence of the Levant in History: Prominent Levant History
- Future of the Levant and the Countries of the Levant
- Conclusion on What is the Levant, the Countries of the Levant, Levant History and Culture
Introduction to What is the Levant and the Countries of the Levant
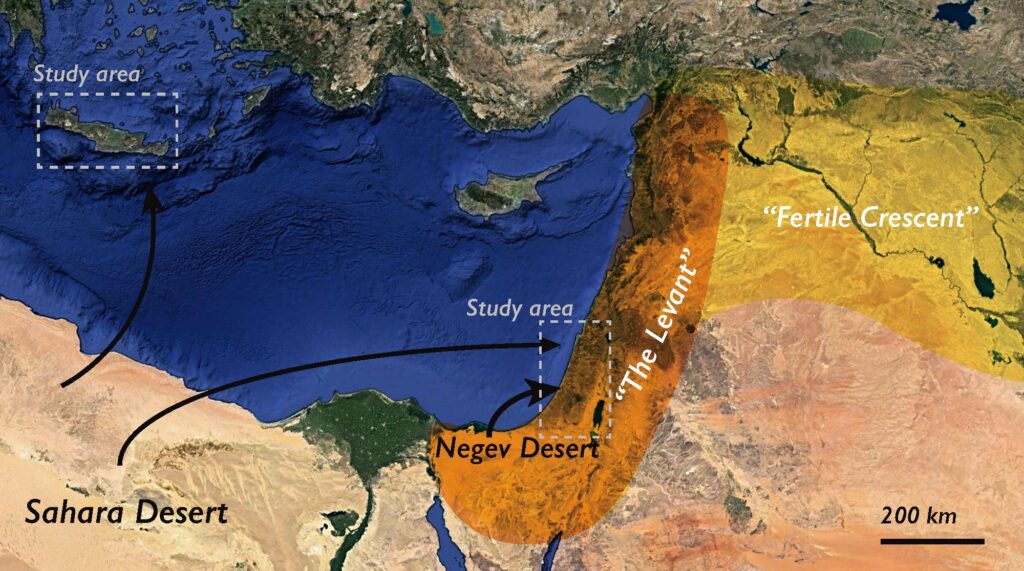
What is the Levant? The Levant is a crucial region, not only geographically but also historically and culturally, located in the Eastern Mediterranean. This area is often described as a “cradle of civilization” because it served as a center for countless cultural, religious, and political developments over thousands of years.
The strategic location of the Levant – the crossroads between three continents: Africa, Asia, and Europe – has transformed it into a melting pot of diverse peoples and traditions. This has significantly contributed to the vast influence of the Levant, shaping global history in a profound way.
This article will help you understand the Levant better, including the countries of the Levant, its prominent geographical features, rich cultural heritage, and the region’s significance in world history as well as current influences.
What is the Concept of the Levant? History of the Levant and its Boundaries
What is the Levant?
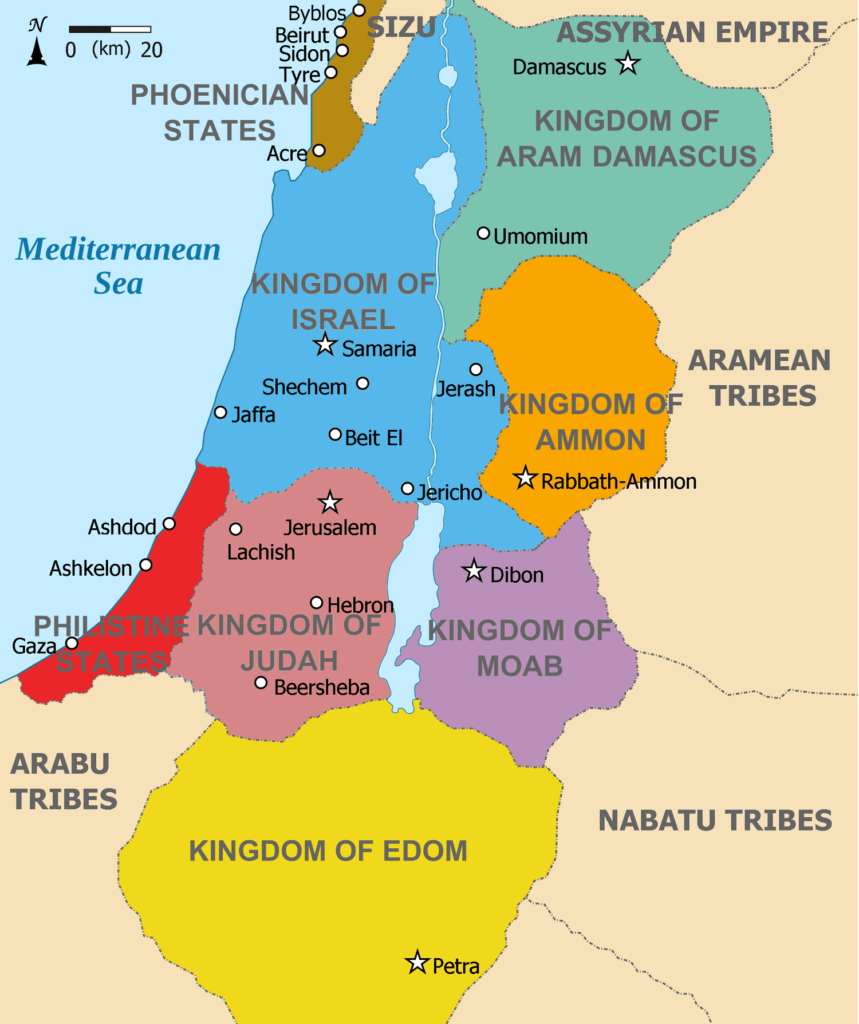
Levant is a term used to refer to the region bordering the Eastern Mediterranean Sea, traditionally including the present-day countries of Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, and Palestine. In broader historical contexts, the Levant sometimes extends to parts of Turkey, the island of Cyprus, and even parts of Iraq and Egypt.
Origin of the term “Levant“ and its historical usage
The word “Levant” originates from the French word lever, meaning “to rise” – referring to the sun rising in the East. Additionally, it is related to the Latin word levare, meaning “to lift” or “to develop”. The term first appeared in English around 1497, referring to the lands in the Eastern Mediterranean, i.e., the areas located East of Italy.
Over time, “Levant” was used to refer to many ancient kingdoms such as Israel, Judah, Ammon, Moab, Aram, and the seafaring nations of Phoenicia and Philistine. This demonstrates the Levant’s long-standing, irreplaceable position as a center of civilization and trade.
Today, “Levant“ is primarily used in archaeology and historical research to describe the land bridge region between Africa and Asia, with boundaries that can vary depending on different contexts.
Countries of the Levant and the Levant in Culture and Archaeology
Countries of the Levant
The Levant primarily includes the following countries:
- Syria
- Has ancient cities such as Damascus – one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world.
- It was a center for many ancient civilizations such as the Arameans. Syrian culture is a blend of Arab, Assyrian, and Mediterranean elements.

Cultural Heritage of Syria
- Lebanon
- Famous for its Phoenician heritage and the historic city of Byblos – one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities.
- Multicultural society with large Christian and Muslim communities. Lebanese cuisine, music, and art are highly valued and widespread in the region.
- Jordan
- Notable for the legendary city of Petra, a landmark of great significance in Biblical history.
- It is an important cultural crossroads, also known for its hospitality and role as a place of refuge.
- Israel
- The city of Jerusalem is a sacred site for the three major religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
- This country is also noted for its ethnic diversity and advanced technological development.
- Palestine
- Includes the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, a center of many historical and political events.
- Cities like Bethlehem or Jericho are of great historical and religious importance.
Furthermore, depending on the research context, the Levant region may include the island of Cyprus, parts of Turkey and Iraq.
The Levant in Culture and Archaeology
The Levant is renowned as a region rich in archaeology and culture with many important sites from ancient civilizations. It features linguistic diversity, including Arabic, Hebrew, Aramaic, Armenian, and ancient Greek. Levant culture is a blend of Mediterranean, Arab, and indigenous elements, clearly shown through its unique cuisine (hummus, tabbouleh, falafel), music, and traditional crafts (intricate mosaic work, art glass, traditional textiles).
Geographical Significance of the Levant and its Boundaries
Geographically, the Levant is located along the Eastern Mediterranean coast, surrounded by several mountain ranges and deserts:
- To the North borders the Taurus Mountains of Turkey
- To the South is the vast Arabian Desert
- To the East borders the region of Mesopotamia
Levant Boundary
An important characteristic of the Levant is its role as a land “bridge” between three continents, serving as a vital strategic corridor for trade, migration, and conquest throughout the ages.
Notable geographical features include:
- Fertile Mediterranean coastline, providing rich land and convenient sea routes
- The majestic Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges
- The Jordan River Valley – including the Dead Sea and the Jordan River, one of the regions with high historical and economic value
This geographical location has made the Levant a focal point of contention for many great empires, while also being a place of intersection and exchange for cultures worldwide.
Culture and Heritage of the Levant in Culture and Archaeology
The Levant is a land that preserves a diverse symphony of culture and religion. It is the center of the world’s three major religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, with sacred cities like Jerusalem, Damascus, and Bethlehem being important pilgrimage sites for millions.
Notable ancient sites and cities:
- Jerusalem, center of many historical and religious events
- Damascus, the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world
- Coastal cities like Tyre and Sidon – playing crucial roles in the Phoenician civilization
- Petra with its exquisitely carved stone structures
- Byblos, one of the oldest cities in the world
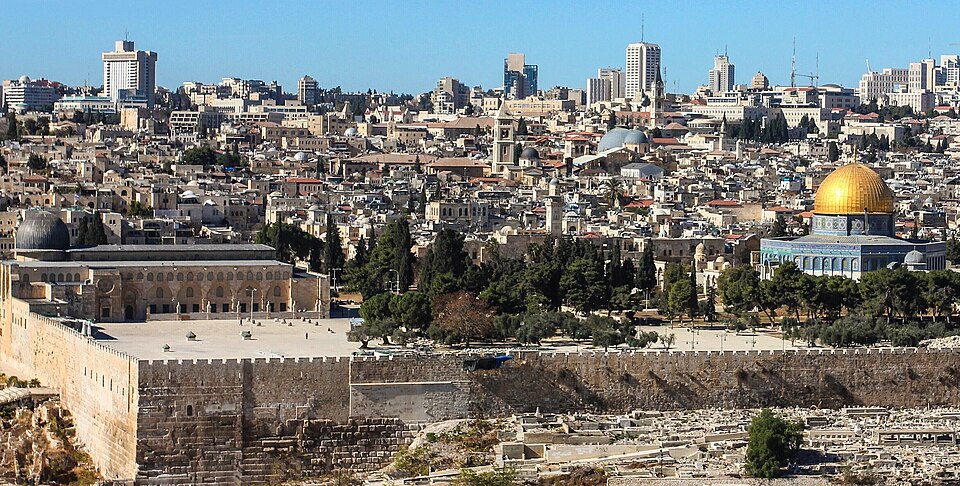

Jerusalem
Linguistically, this region is very diverse with modern Arabic, ancient and modern Hebrew, Aramaic – once a common language in ancient times, along with other languages such as Armenian and Greek.
The vibrant culinary culture of the Levant includes:
- Hummus dish made from chickpeas
- Tabbouleh, a fresh herb salad
- Falafel, crispy fried chickpea patties
In addition, handicrafts such as intricate mosaics, hand-blown glass, and traditional textile products are distinctive features not to be missed.
Influence of the Levant in History: Prominent Levant History
The Levant has a history spanning tens of thousands of years, being one of the first cradles of agriculture and the earliest cities in the world.
Many great civilizations have existed and developed here:
- The Canaanites, Phoenicians, Israelites, and Arameans were important ancient ethnic groups.
- Empires such as ancient Egypt, Assyria, Babylon, Persia, Greece, Rome, Byzantium, and the Islamic caliphates all vied for control and left profound marks.
Important contributions of the Levant:
- Popularization of Semitic languages and the development of the first alphabets, among which the Phoenician alphabet strongly influenced later Western writing systems.
- Religious and philosophical events forming the basis for the three major religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
- The Crusades, the Ottoman period, and the modern Arab-Israeli conflict have also left lasting impacts to this day.
Through trade routes, population movements, and wars, the Levant connected and influenced civilizations in Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Future of the Levant and the Countries of the Levant
Currently, the Levant continues to face many serious geopolitical challenges:
- The protracted Syrian civil war, causing a severe refugee crisis
- The ongoing conflict between Israel and Palestine
- Issues concerning land sovereignty, resource rights, and national identity
The future of this region largely depends on the ability to reconcile conflicts, promote economic development, and preserve its unique cultural heritage.
In the context of increasing globalization, the strategic position of the Levant as a crossroads for trade, spreading ideas and cultural experiences remains of significant value.

Conclusion on What is the Levant, the Countries of the Levant, Levant History and Culture
In summary, the Levant is a land of immense historical, cultural, and geopolitical value. Comprising the countries of Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, and Palestine, this region is not only a bridge between continents but also a nurturing ground for a diverse and complex civilization.
With its distinctive geographical boundaries, rich archaeological heritage, and influences throughout history, the Levant continues to hold a significant role on the world map.
If you are interested in ancient history, religion, or international issues, a deeper understanding of the Levant will open up many new perspectives. You can refer to further in-depth research materials, archaeological reports, or updated news about the Middle East to gain a more comprehensive understanding of this legendary region.
Further reading references:
- History and geography of the Levant on Wikipedia
- Cultural and archaeological studies on the PCRF website
- Analysis articles on Middle Eastern history on international academic websites
The Levant is not just a land – It is a symbol of cultural crossroads and unparalleled diverse identity.
See also:
Should you learn Arabic? Where to learn Arabic?
The Arab Market: Are you missing out on the potential market of 422 million people?